Post Time: 2025-07-18
The management of blood sugar fluctuations is a crucial aspect of living with diabetes. When left unmanaged, these fluctuations can lead to serious health complications such as heart disease and nerve damage.
Understanding the Rhythm of Your Body When it comes to maintaining a healthy blood sugar range, diet plays a significant role in regulating these levels. Certain foods have been found to help stabilize blood sugar by providing sustained energy releases. Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread are excellent sources of fiber that can slow down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream.
The American Diabetes Association recommends incorporating 25-30 grams of fiber per day in a person's diet. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids such as salmon, walnuts, and chia seeds have been found to improve insulin sensitivity which is key to maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Another essential component in managing blood sugar fluctuations is regular exercise. Physical activity helps the body use up excess glucose thereby reducing its load on the pancreas and preventing unnecessary spikes in blood sugar levels. It also enhances insulin sensitivity making it easier for glucose to enter cells and thus reducing symptoms associated with high or low blood sugar episodes.
A study published in Diabetes Care found that exercising even as little as 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week improved glycemic control significantly among individuals living with diabetes. Moreover, resistance training is beneficial in maintaining muscle mass which also plays a role in regulating insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels helps to identify potential fluctuations allowing the individual or their healthcare provider to take prompt action. Regular tracking can be done using glucometers that measure interstitial fluid glucose levels providing data on trends over time as well as other tools like continuous glucose monitors which track real-time changes in blood glucose levels and send alerts when thresholds are exceeded.
Proper diet along with regular physical activity is the most effective approach to maintaining a stable range. This may require significant lifestyle adjustments, but its benefits extend far beyond just managing diabetes symptoms; by reducing risk factors associated with metabolic syndrome such as hypertension cardiovascular disease, high cholesterol individuals can maintain overall optimal health thereby extending lifespan and ensuring improved quality of life.
Regaining Control Through Nutrition
While the impact physical activity has on blood sugar levels is well documented, a balanced diet plays an equally significant role in maintaining healthy glucose metabolism. Foods that are rich in fiber like beans lentils fruits and vegetables contribute to sustained energy releases as opposed to simple carbohydrates found primarily in sugary foods leading to spikes in blood sugar.
Certain food groups should be avoided by individuals living with diabetes due to their high impact on insulin resistance, for example processed meats which have been linked directly through scientific research. Maintaining optimal levels of body fat and muscle mass via a balanced diet combined with regular exercise is crucial as the more significant an individual's percentage body fat above 25%, greater are they susceptible to developing issues related specifically due blood sugar management complications.
Managing Blood Sugar Fluctuations effectively can seem like a daunting task, but by understanding your own biological needs incorporating healthy food choices engaging in sustainable physical activities and maintaining regular tracking of physiological health will contribute substantially towards stabilizing glucose levels thereby reducing associated risks for better quality living.
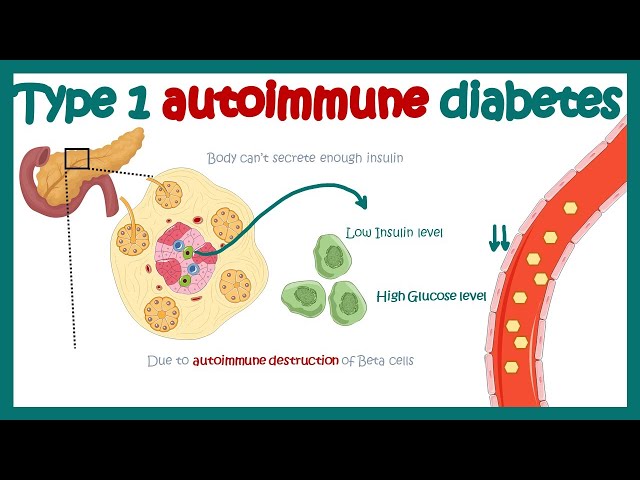
A chronic condition in which the a1c blood sugar pancreas produces little or no insulin. It 5.5 blood sugar conversion typically appears in adolescence. Symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, hunger, fatigue and blurred vision. Treatment aims at 249 blood sugar maintaining normal blood sugar levels through regular monitoring, insulin therapy, diet and exercise.