Post Time: 2025-07-18
When it comes to blood sugar levels, anything below 54 is considered hypoglycemia or low blood sugar. A reading of exactly 35 is an extremely alarming sign that requires immediate medical attention.
The body's primary source of energy is glucose, and when the level falls too low, the brain starts using stored glycogen for fuel. If this condition persists, it can lead to serious complications such as seizures, coma, or even death.
A blood sugar reading of 35 typically indicates a lack of insulin in the body or that there's not enough glucose being absorbed from food. This could be due to various factors including certain medications like sulfonylureas and insulin injections for diabetes management.
People with type-1 diabetes need regular doses of insulin, so it can become challenging to maintain normal levels, especially during times of stress or other physiological changes.
The brain needs a constant supply of glucose to function properly. It relies on stored glycogen as an immediate energy source when the blood sugar level drops. If this condition becomes chronic due to frequent episodes of low blood sugar readings such as 35, it may lead to damage in certain areas like memory and cognitive functions.
Managing Blood Sugar Spikes with Effective Lifestyle Changes
Maintaining optimal health involves keeping blood glucose levels within a narrow range throughout the day. To manage blood sugar spikes effectively one must incorporate various healthy lifestyle changes that play an important role in controlling this fluctuation of readings, especially those which fall below 100 mg/dl like the reading mentioned.
Incorporating low to moderate-intensity aerobic exercises for at least half-hour each week significantly improves insulin sensitivity and reduces inflammation. High-fiber foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes should also be included in one's daily diet since they are more slowly digested which gradually increases blood sugar levels rather than causing spikes.
The best part about making these lifestyle changes is that most people will experience a reduction in symptoms within just several weeks and this leads them to maintain a regular routine with their medications for better outcomes of managing low or high readings. This includes eating at least three times, but it's also important not overeat; portion control really makes the difference when trying out new recipes.
Stabilizing Blood Sugar Levels with Balanced Nutrition
The impact that nutrition has on blood sugar levels can vary significantly depending upon what kind and quantity of food is consumed in a given day. Therefore maintaining balanced meals throughout all four eating periods will prevent significant drops as seen at 35 mg/dl because such low reading may indicate severe condition, hence require immediate assistance.
When making changes to the way we eat it's essential that we do so gradually rather than drastically switching everything over one week; this approach usually leads people back towards unhealthy routines faster due mainly poor adherence patterns post dietary intervention.
Eating small, evenly spaced meals throughout the day is not only practical but also has been shown in research studies worldwide as effective at minimizing fluctuations within blood glucose levels - even when experiencing extreme dips such low readings of 35mg/dl.
A healthy balanced meal consists of a variety of foods including some carbs for energy like whole grain breads pasta rice; proteins from meat poultry fish eggs dairy products legumes tofu nuts seeds to provide necessary building blocks along with veggies offering fiber antioxidants other nutrients required by human body system functioning optimally always under control maintaining tight range blood glucose monitoring thus preventing complications down line.
Balancing Stress and Blood Sugar Readings
Chronic stress is associated with increased cortisol levels which lead directly lowered effectiveness in insulin signaling mechanisms inside cells leading elevated blood sugar despite high consumption; people may require constant checking by glucometer so that right medication adjustment according symptoms occurs timely manner before worsening condition sets root itself causing irreversible damages.
Exercise regularly does stimulate production of neurotransmitters such serotonin and endorphins promoting relaxation mood stabilization thus countering adverse psychological stress impacts indirectly regulating hormone responses within the body ensuring balanced sugar utilization efficiency - all without over-exertion since this increases blood glucose due release energy stores stored fat muscle tissues etc leading high spikes seen during intense activity periods especially those below desired range values close fifty mg/dl mark thirtyfive considered lowest level hypoglycemia defined.
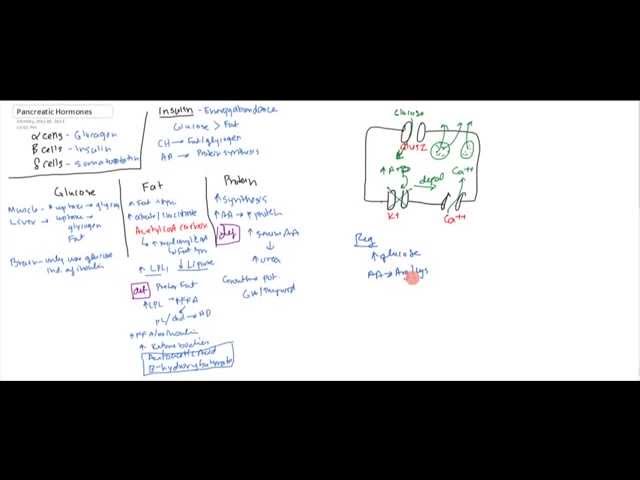
The endocrine pancreas hormones such as Insulin, Glucagon, and somatostain physiology and pathophysiology explained for USMLE Step 1. is made up of 3 types of cells. Alpha cells secrete glucagon, Beta cells secrete insulin and Delta cells secrete somatostatin. INSULIN Generally speaking insulin is designed for energy abundance. So your body prefers to use glucose rather than fats for energy. The body will use CH instead of fat and glycogen. And use Amino Acids for protein synthesis. GLUCOSE Muscle will have increase uptake to make glycogen in the muscle. In the liver it will be used for uptake to use fast blood sugar test for glycogen and fat. Brain will only use glucose blood sugar 330 mg dl and this is independent of insulin. FAT Increase fat storage. Increase citrate and isocitrate. Increase AcetylCoA Carboxylase. This increase malonyl CoA which will increase Fat synthesis. This will increase Lipoprotein lilpase and decrease lipase. In Deficiency you prefer fats so you increase lipoprotein lipase which increase Free Fatty Acids. This will become phospholipids and cholesterol leading to heart disease. When there is Free Fatty Acids without insulin this will increase Ketone bodies (Acetoacetic Acid and B-hydroxyacetate). PROTEIN Increase synthesis and storage of protein. Increase AA and Increase Protein synthesis. In deficiency there is increase serum AA and increase urea in urine. It also increase effect on Growth Hormone. MECHANISM OF ACTION of BETA Cell When Glucose comes in this increases ATP and blocks Potassium channel. This depolarizes and causes opening of Calcium channel. Regulated by glucose, Amino Acids, and GIT hormones. GLUCAGON This hormone is expressed when glucose is low. Therefore it will increase gluconeogenesis by converting Amino acids into glucose and converted fats into glucose. Increase cAMP which will increase Phorphokinase which will increase phorphorylase and increase glucose phosphate. Only small amount of glucose is necessary to have greater effects does cheese lower blood sugar because of amplification. At really high concentrations it can increase heart contraction, increase blood flow to organs, increase bile secretion an block gastric acid. SOMATOSTATIN REgulated by high glucose, Amino Acids, Fatty Acids and GIT hormones. Effects of somatostatin - decrease insulin and glucagon. Decreases motility of duodenum, stomach and gallbladder. Decreases secretion and absorption in GIT.